If you’re considering the worth of UDP vs TCP , we’re going to assume that you’re already familiar with the all-important transport layer. As with everything, both protocols has advantages and disadvantages. To form a competent decision, though, it’s significant to recognize the key differences between the two.
What is TCP?
The Transmission Control Protocol is one of the first protocols that enhance the IP (Internet Protocol). The Internet Protocol forms the Internet work. It’s the basis of data transport.
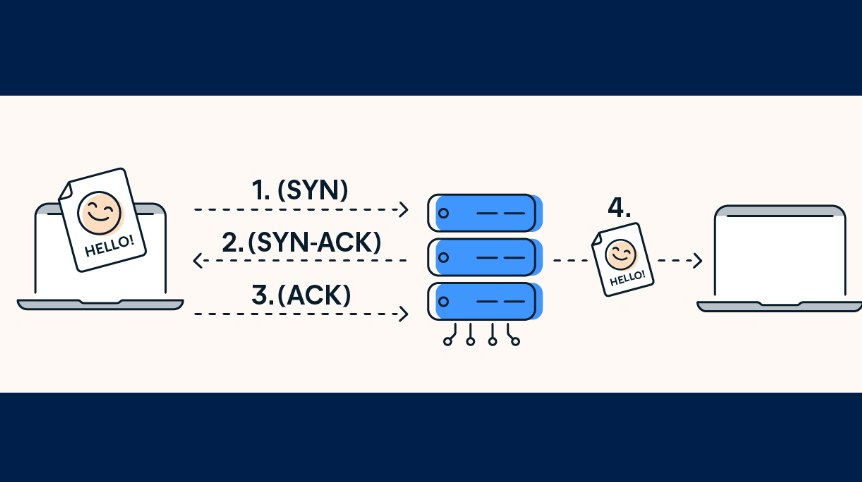
However, the TCP is the protocol overseen for smooth data packet transmission. This means that it resolves issues like loss of packets, packets that are out of order, corrupted packets, and duplicates.
Think when a data packet is lost or duplicated. In that case, TCP requests other transmissions of the data that isn’t there or is out of order.
The TCP regulates the transmission, and we get entire data when we go online as of it. It’s a protocol that is a division of any operating system today.
What is UDP?
The User Datagram Protocol is also one of the most significant protocols in the Internet Protocol Suite. It’s has a small difference from TCP.
The UDP doesn’t send requests to other members in the network. There’s no necessity for communication before the transmission. This tells that it can send messages, datagrams to other web members.
Datagrams are very main units of transfer. When a datagram is transferred, there’s no requirement for any prior communication. It only requires an address for delivery.
Through, the delivery isn’t guaranteed, and it won’t be confirmed either. It’s not as dependable as the TCP. That’s why these two work together consecutively or intermittently to assists the requirements of the users.
To put it simply, the UDP is a connectionless program. It can send tons of packets to multiple users simultaneously, as it is much quicker than the TCP, but it is also untrustworthy. It’s very suitable for streaming services
Difference Between : UDP VS TCP
| Basis | Transmission control protocol (TCP) | User datagram protocol (UDP) |
| Service Types | TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. This means that the communicating devices must arise a connection before transmitting data and must close the connection after transmitting the data. | UDP is the Datagram-oriented protocol. This is because there is no overhead for opening a connection, continuing a connection, and terminating a connection. UDP is cost-effective for broadcast and multicast types of network transmission. |
| Reliability | TCP is dependable as it guarantees the delivery of data to the end router. | The delivery of data to the end cannot be guaranteed in UDP. |
| Error checking mechanism | TCP offers huge error-checking mechanisms. It is because it gives flow control and recognition of data. | UDP has only the primary error checking mechanism using checksums. |
| Acknowledgment | An acknowledgement segment exists. | There is no acknowledgement segment. |
| Sequence | Sequencing of data is an aspect of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). this means that packets come in order at the receiver. | Sequencing of data is not present in UDP. If the order is needed, it has to be managed by the application layer. |
| Speed | TCP is similarly moderate to UDP. | UDP is rapid, easier, and more efficient than TCP. |
| Retransmission | Retransmission of lost packets is possible in TCP, but not in UDP. | Retransmission of lost packets is not possible in the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). |
| Header Length | It has a (20-60) bytes variable length header. | It has an 8 bytes fixed-length header. |
| Weight | TCP is heavy-weight. | UDP is lightweight. |
| Handshaking Techniques | Uses handshakes such as SYN, ACK, SYN-ACK | It’s a connectionless protocol i.e. No handshake |
| Broadcasting | TCP doesn’t support Broadcasting. | UDP supports Broadcasting. |
| Protocols | TCP is operated by HTTP, HTTPs, FTP, SMTP and Telnet. | UDP is operated by DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, and VoIP. |
| Stream Type | The TCP connection is a byte stream. | UDP connection is a message stream. |
| Overhead | Low but higher than UDP. | Very low. |
Streaming starts with the first buffering. After that, it extends a steady-state, where buffering and the video continues doing their thing simultaneously.
Astonishingly, Video on demand uses both UDP and TCP connections. The ratio of the uses of these two protocols is 62.5 % UDP sessions and 37.5 % TCP sessions.
So, why does VOD runs on UDP than TCP protocol?
Well, as we said before, UDP doesn’t need communication before it sends data packets. This creates UDP ideal for streaming live videos.
However, the TCP secures the data is dedicated and complete, so it accounts for data loss.
When we’re discussing a video on demand as well. This is where UDP surely has an advantage over TCP.
Video streaming requires UDP because there’s small communication between the host and the users when watching a live stream. It’s definitely quick loading, but it can come with some nerves.
That’s what happens when using an untrustworthy protocol. However, both protocols belong to the same thing that creates smooth data packet transmission.
We hope this blog has helped clarify the purpose of a UDP and TCP for Video on demand(VOD) and the difference between UDP and TCP protocol. We trust that you are prepared to choose and use the right protocol for your video business needs.

Leave a Reply to Himesh Cancel reply