Hello, innovators!
According to Experro, the headless CMS market is expected to grow from $605 million in 2022 to $3.8 billion by 2032, reflecting a significant rise in adoption.
Choosing the right content management system is crucial for building modern websites and applications. A key debate in this space is Headless vs Decoupled CMS, two architectures that are often confused but have distinct differences.
While both separate the front-end and back-end to some extent, their flexibility, integration capabilities, and use cases vary significantly.
In this article, we’ll break down the headless vs. decoupled CMS debate, exploring their core differences, advantages, and ideal use cases to help you determine the best approach for your project.
Key Takeaways on Headless vs decoupled cms
- Headless vs Decoupled CMS differs in flexibility headless fully separates content and presentation, while decoupled retains some front-end control.
- Headless CMS vs decoupled CMS impacts scalability headless CMS supports omnichannel experiences, whereas decoupled CMS offers structured expansion with limited built-in front-end capabilities.
- Headless architecture demands a custom-built front-end, while decoupled architecture offers pre-designed templates with API-driven content delivery for flexibility.
- A headless CMS gives developers full creative freedom to use any framework, whereas a decoupled CMS imposes certain design and customization limits.
- Businesses aiming for seamless omnichannel content delivery benefit from a headless CMS, while those wanting some front-end control may choose a decoupled CMS.
Power Your Ecommerce with Headless CMS!
Headless vs Decoupled CMS: A Primary Key Difference
When comparing headless CMS and decoupled CMS, it’s important to understand their key differences. Each offers unique advantages for content management, flexibility, and frontend development capabilities. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | Headless CMS | Decoupled CMS |
| Definition | A “content as a service” platform where content is stored in the cloud and delivered via APIs. | A CMS with both backend and frontend, but the two remain separate. |
| Frontend Dependency | No built-in frontend; developers can use any technology (React, Angular, etc.). | Comes with a frontend but allows custom frontend development. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility since the frontend is fully customizable. | Some flexibility, but with pre-built frontend options. |
| Ease of Setup | Easier to configure and integrate with modern tech stacks. | More complex setup, often requiring additional configuration. |
| Common Backend | Typically API-driven CMS platforms. | Often traditional CMS platforms like WordPress or Drupal. |
| Best For | Businesses need omnichannel experiences with complete frontend control. | Those wanting a structured CMS with some frontend customization. |
Headless CMS vs decoupled CMS: Architectural differences
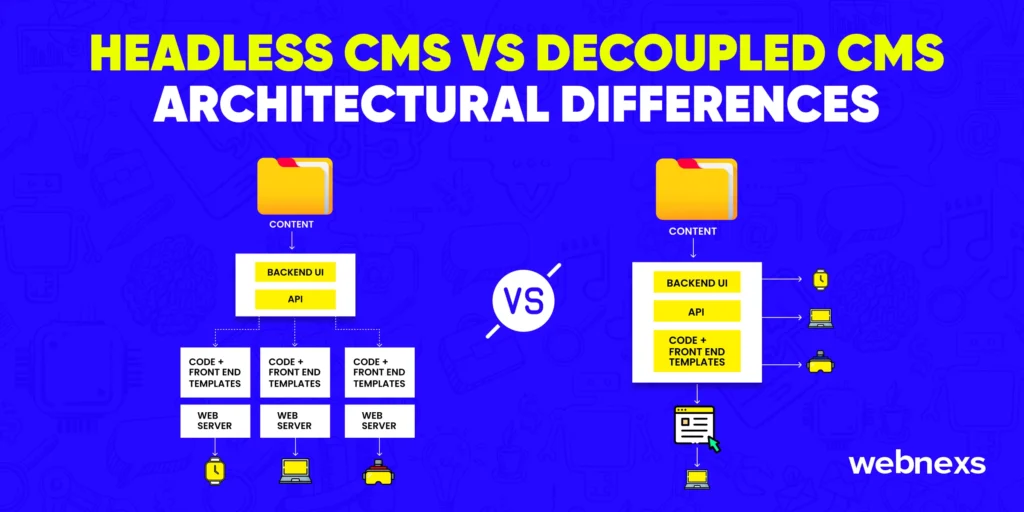
1. Market Growth
- Headless CMS Architecture: Projected to reach $1.6 billion by 2026 with a 20% CAGR.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Expected to hit $1.2 billion by 2025, emphasizing flexible content management and delivery.
2. API-Driven
- Headless CMS Architecture: Content is stored in a central backend and accessed through APIs (75% usage rate) for adaptability across multiple platforms.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Backend and frontend interact via APIs (65% usage rate) to fetch and update content independently.
3. Frontend Approach
- Headless CMS Architecture: Lacks a predefined presentation layer, giving developers full control over content delivery.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Provides frontend independence (70%), where the frontend operates separately but connects via APIs.
4. Flexible Content Management
- Headless CMS Architecture: Developers can retrieve, update, and display content independently of any specific frontend framework.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Ensures backend content management, where content is created, edited, and organized without controlling its presentation.
5. Component Breakdown
- Headless CMS Architecture:
– APIs (75%)
– Backend systems (60%)
– Databases (50%) for content storage
- Decoupled CMS Architecture:
– Frontend interfaces (70%)
– APIs (65%)
– Backend systems (60%)
– Secure databases (50%)
Key Components of a Headless CMS
1. API Connectivity
- Headless CMS Architecture: Links the backend to multiple digital platforms.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Bridges backend content with frontend applications.
2. Backend CMS
- Headless CMS Architecture: Central hub for content creation and management.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Content is created and structured separately from the presentation layer.
3. Database Storage
- Headless CMS Architecture: Manages and secures content and digital assets.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Stores and protects all digital content.
4. Frontend Interface
- Headless CMS Architecture: Lacks a predefined frontend, giving developers full control over content delivery.
- Decoupled CMS Architecture: Displays content on websites, apps, or other platforms.
Architectural Differences at a Glance
The main differences between these two systems can be explained as follows:
Headless CMS: In a headless setup, the CMS is paired with an API. This API lets you create applications (like mobile apps, websites, or web apps) that get data from the backend.
Decoupled CMS: A decoupled setup separates the front end (what users see) from the back end (where the data is stored) using an API. You can use the front-end and back-end separately or together in your app.
The key difference is that headless CMS is reactive it only provides content as data, without displaying it directly to users. Decoupled CMS, however, processes content at the backend before sending it out to different channels for display.
Build Smarter with Headless Architecture!
The problem with traditional CMS solutions

Traditional CMS platforms have been around since the late 1990s. They’re mainly used to manage and display content on websites. These systems often use templates to help content creators design, publish, and organize their work easily.
A traditional CMS has two main parts: the front end and the back end.
The front end is what users see when they visit a website or app, while the back end is where all the content is stored and organized.
The issue with this setup is that the front-end and back-end are closely linked. So, if you make a change to one part, you often have to adjust the other part as well, which can be a hassle.
In systems like Drupal, Joomla, and WordPress, both the back-end and front-end are tightly connected. While this setup is easy to use and cost-effective, it does come with some downsides, such as:
- Updating one part can be risky for the whole system
- Upgrading the back-end often requires changes to the front-end too
- You can’t update or change the front-end and back-end separately because they are so connected
- It’s very difficult to scale the system.
Here’s a more detailed explanation of what does Headless Architecture and Decoupled Architecture mean, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
What Does Headless Architecture Mean?

According to a survey, 73% of businesses have adopted headless architecture, showing a 14% growth since 2021. Additionally, 98% of businesses not yet using headless plan to implement it within 12 months.
When asking what is headless architecture, it refers to an approach where the front end and back end of a website or application are separated. In other words, the website or application is “headless” because it doesn’t have a traditional front-end.
Instead, the back-end provides data through a REST API to a separate frontend, which can be built using any technology or framework and offers a flexible user interface. This headless architecture allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as the front end can be easily updated or replaced without affecting the back end.
Advantages of a Headless CMS Architecture
1. Great Flexibility
A headless CMS eliminates concerns about how content will align with a website’s design. Content is created in a central location and published to various websites or interfaces as needed. This system also allows you to choose the tools and technologies that best suit your needs and easily integrate with new ones.
2. Support for Multiple Channels
In a headless CMS, content and code are separated, enabling a single instance to serve multiple digital platforms like mobile apps, kiosks, smartwatches, and digital signage, without duplicating content. You can send content to multiple devices and platforms simultaneously, and developers can quickly build new distribution channels as necessary.
3. Lower Costs
A headless CMS simplifies the process of building and improving websites. Developers can use APIs to connect different parts of your tech stack to the CMS. There’s no need to wait for templates before creating new content, and you can reduce upfront costs by starting with a smaller, more manageable project instead of a full-scale website development.
4. Easier Management
Managing and distributing content across websites, mobile apps, and IoT devices is straightforward with a headless CMS. The separation of the backend and frontend allows you to make changes or solve problems on the backend without interrupting the user experience on the site.
5. Better Security
Opting for a headless CMS improves security by reducing the risk of attacks, such as DDoS, since the publishing platform isn’t directly linked to the CMS database. It also facilitates safe integration with third-party solutions.
Actionable Insights: Adopt a headless CMS to enhance flexibility, streamline multi-channel content distribution, reduce costs, simplify management, and improve security, ensuring a seamless user experience across all digital platforms.
Embrace Innovation with Headless CMS Architecture Now!
Disadvantages of a headless CMS solution

1. No Presentation Layer
A key disadvantage of a headless CMS is that it doesn’t have built-in tools for displaying content. It also requires more technical expertise, especially during the initial setup, compared to traditional CMS solutions.
2. Higher Complexity
Using a headless CMS can be complicated and may require skilled developers. You’ll often need to manage multiple codebases, one for each front-end that the API connects to.
3. Higher Costs
Due to its fragmented technology setup, implementing and maintaining a headless CMS can be more expensive.
What Does Decoupled Architecture Mean?

Experts predict that by 2025, 60% of ecommerce businesses will adopt decoupled architecture, driven by a 30% increase in demand for flexible, customizable solutions. 50% of large enterprises are expected to migrate to this model for improved scalability and performance.
Decoupled commerce architecture, on the other hand, refers to an approach where the front-end and back-end are still separated, but the front end is not completely separate from the back end. Instead, the front end is tightly coupled with the back end, but only to a certain extent.
In a decoupled architecture, the front end can access certain back-end features, such as business logic, authentication, or user management, while still operating independently, similar to a headless architecture. This allows for more control and customization over the front-end, while still maintaining the benefits of a separate back-end, much like in a microservices architecture.
Advantages of a decoupled CMS solution

1. More Flexibility
A decoupled CMS, you’re not limited to pre-made templates. You can work with any designer or developer to create a custom user interface that fits your needs.
2. Better Performance
A decoupled CMS improves website speed and scalability by distributing traffic across different systems. Features like caching and auto-scaling help maintain high performance, even during peak traffic.
3. Stronger Security
Since the content creation and delivery systems are separate, you can add firewalls to protect your network. This setup also lowers the risk of cyber threats like DDoS or SQL injection attacks. Unlike traditional CMS platforms, security issues on the front end won’t affect the entire system.
4. Flexible Deployment
You can publish content anywhere on a separate server, a cloud environment, or a content delivery network (CDN). You can also manage multiple publishing sites and release updates instantly.
5. Easier Scalability
A decoupled CMS lets you build the front-end using any technology, such as React, Angular, or Vue.js. Since the back-end and front-end are separate, maintenance and updates won’t cause downtime. You can scale your CMS by upgrading the back end or adding resources without affecting performance.
Actionable Insights: Adopt a decoupled CMS for enhanced flexibility, improved performance, stronger security, and flexible deployment. This approach simplifies scalability and allows seamless updates without downtime, ensuring efficient content management across platforms.
Upgrade Your Content with Decoupled CMS!
Disadvantages of a decoupled CMS
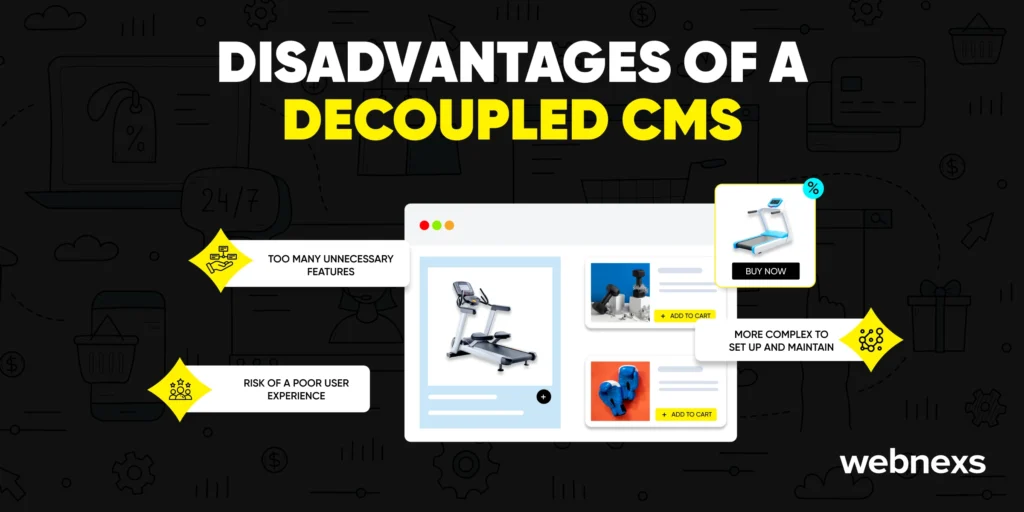
1. More Complex to Set Up and Maintain
A decoupled CMS requires more configuration and management than a headless CMS. It’s not as straightforward, making setup and maintenance more time-consuming.
2. Too Many Unnecessary Features
Decoupled CMS platforms come with a wide range of features, many of which may not be useful for smaller teams or individual developers. Large enterprises might need them, but for others, they can add complexity.
3. Not Fully Developer-Friendly
Unlike headless CMS platforms, which prioritize developers, decoupled CMSs try to balance the needs of marketers and developers. This can sometimes result in constraints that make development more frustrating.
4. Risk of a Poor User Experience
Developers may be forced to use predefined templates rather than fully customizing the front-end. If the front-end and backend aren’t well integrated, users may experience slower load times or inconsistent interfaces.
5. Steeper Learning Curve
Working with a decoupled CMS requires advanced technical skills, especially when deploying content across multiple platforms. It’s best suited for teams with dedicated front-end specialists rather than general full-stack developers.
While a decoupled CMS offers flexibility, these challenges should be considered before choosing it over a headless CMS.
Why Choosing Headless and Decoupled Commerce Architecture from Webnexs?
Webnexs is a platform that supports headless and decoupled web development architectures. With headless architecture, developers can build custom frontend interfaces and integrate them with the platform’s backend system using REST APIs, a webhook service, or GraphQL integration.
This headless website architecture offers greater flexibility and control over the user interface and overall user experience, similar to a decoupled website. On the other hand, cms decoupled architecture allows developers to separate the front-end and back-end of a website, enabling them to work independently. This results in faster development times and easier maintenance.
By supporting both architectures, including the headless architecture pattern, WordPress, and GraphQL integration, Webnexs empowers developers to create innovative and dynamic websites that meet the needs of businesses and users alike, highlighting the advantages of the headless vs decoupled CMS debate.
Conclusion
When comparing headless vs decoupled CMS, the best choice depends on your business requirements. A headless software provides maximum flexibility, giving you full control over content presentation across different platforms.
In contrast, a decoupled CMS offers a hybrid approach, combining some flexibility with built-in front-end capabilities.
If you’re unsure which CMS fits your needs, Webnexs is here to help. Contact us today to find the right solution and streamline your content management process!

